Color transformation from Bayer to RGB
Published at February 17, 2020 · Last Modified at November 19, 2021 · 4 min read · Tags: bayer rgb computer-vision
Color transformation from Bayer to RGB
Published at February 17, 2020 · Last Modified at November 19, 2021 · 4 min read · Tags: bayer rgb computer-vision
A Bayer filter mosaic is a color filter array (CFA) for arranging RGB color filters on a square grid of photosensors. Its particular arrangement of color filters is used in most single-chip digital image sensors used in digital cameras, camcorders, and scanners to create a color image. The filter pattern is 50% green, 25% red and 25% blue - see here.
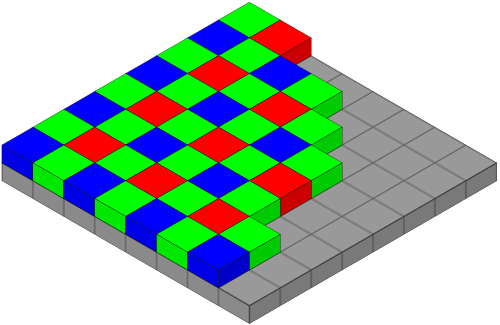
The conversion algorithm is based on simple linear interpolation of pixels to find the missing value. Since Bayer filter dived into 4 pixels (red, green, green, blue), there are four types of equations for each pixel in the square.
The following is RGB triple for the pixels on red channel: $$ RGB_{} = ( I_{n,m} , \frac{I_{n-1,m} +I_{n+1,m}+I_{n,m-1} + I_{n,m+1}}{4} , \frac{I_{n-1,m-1} +I_{n+1,m+1}+I_{n-1,m+1} + I_{n+1,m-1}}{4} ) $$
The following is RGB triple for the pixels on green1 channel:
The following is RGB triple for the pixels on green2 channel:
The following is RGB triple for the pixels on blue channel:
where $$ I_{n,m} $$ is raw bayer pixel
Implementation using python including that modules: matplotlib, numpy,cv2. To install these modules with pip:
pip install matplotlib --user
pip install numpy --user
#pip install cv2 --user - not sure this will work , I did it with the gentoo package manager (in debian/ubuntu you can try apt-cache search)
Some images to work with can be download from here 1 2 3 4
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import cv2
file_path = 'path-to-bayer.raw'
imrows = 540
imcols = 600
imsize = imrows*imcols
with open(file_path, "rb") as rawimage:
bayer_img = np.fromfile(rawimage, np.dtype('u1'), imsize).reshape((imrows, imcols))
def pixel (img):
img = img.astype(np.float64)
pixel = lambda x,y : {
0: [ img[x][y] , (img[x][y-1] + img[x-1][y] + img[x+1][y] + img[x][y+1]) / 4 , (img[x-1][y-1] + img[x+1][y-1] + img[x-1][y+1] + img[x+1][y+1]) / 4 ] ,
1: [ (img[x-1][y] + img[x+1][y]) / 2,img[x][y] , (img[x][y-1] + img[x][y+1]) / 2 ],
2: [(img[x][y-1] + img[x][y+1]) / 2 ,img[x][y], (img[x-1][y] + img[x+1][y]) / 2],
3: [(img[x-1][y-1] + img[x+1][y-1] + img[x-1][y+1] + img[x+1][y+1]) / 4 , (img[x][y-1] + img[x-1][y] + img[x+1][y] + img[x][y+1]) / 4 ,img[x][y] ]
} [ x % 2 + (y % 2)*2]
res = np.zeros ( [ np.size(img,0) , np.size(img,1) , 3] )
for x in range (1,np.size(img,0)-2):
for y in range (1,np.size(img,1)-2):
p = pixel(x,y)
p.reverse();
res[x][y] = p
res = res.astype(np.uint8)
return res
def channel_break (img):
img = img.astype(np.float64)
red=np.copy (img);red [1::2,:]=0;red[:,1::2]=0
blue=np.copy (img);blue [0::2,:]=0;blue[:,0::2]=0
green=np.copy (img);green [0::2,0::2]=0;green [1::2,1::2]=0;
red = red.astype(np.float64)
blue = blue.astype(np.float64)
green = green.astype(np.float64)
return (red,green,blue)
def rgb2gray(img):
res = np.zeros ( [ np.size(img,0) , np.size(img,1) , 3] )
res = res.astype(np.float64)
for x in range (1,np.size(img,0)-1):
for y in range (1,np.size(img,1)-1):
res[x][y]=img[x][y][0]*0 + img[x][y][1]*0.5 + img[x][y][2]*0.5;
res = res.astype(np.uint8)
return res
# plot bayer imager
plt.imshow(bayer_img)
plt.title ('bayer img')
plt.imsave('bayer_img.png', bayer_img)
#plt.show()
# this algorithm conversion
rgb_res = pixel (bayer_img)
plt.imshow(rgb_res)
plt.title ('the article conversion')
plt.imsave('the_article_conversion.png', rgb_res)
#plt.show()
# open cv conversion
colour = cv2.cvtColor(bayer_img, cv2.COLOR_BAYER_BG2BGR)
plt.imshow(colour)
plt.title ('color image by open cv')
plt.imsave('color_image_by_opencv.png', colour)
#plt.show()
# convert to gray level
gray = rgb2gray(rgb_res)
plt.imshow(gray)
plt.title ('gray conversion')
plt.imsave('gray_level.png', gray)
#plt.show()
# break to RGB channels
RGB = channel_break(bayer_img)
blue_only = pixel (RGB[0])
plt.imshow(blue_only)
plt.title ('blue only')
plt.imsave('blue_only.png',blue_only)
plt.show()
green_only = pixel (RGB[1])
plt.imshow(green_only)
plt.title ('green only')
plt.imsave('green_only.png',green_only)
plt.show()
red_only = pixel (RGB[2])
plt.imshow(red_only)
plt.title ('red only')
plt.imsave('red_only.png',red_only)
plt.show()
#plt.show()

Raw Bayer Image

Conversion to RGB

Conversion by OpenCV
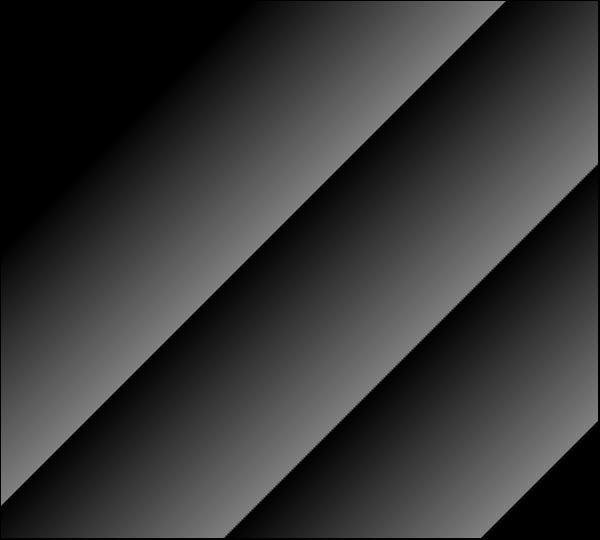

Conversion to Gray
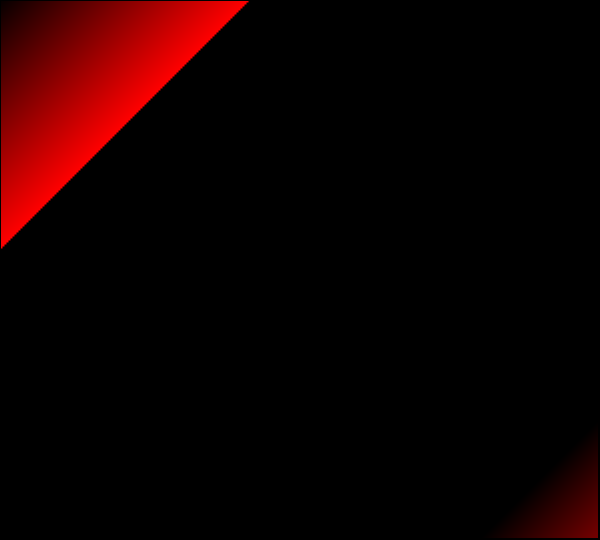

Red Only
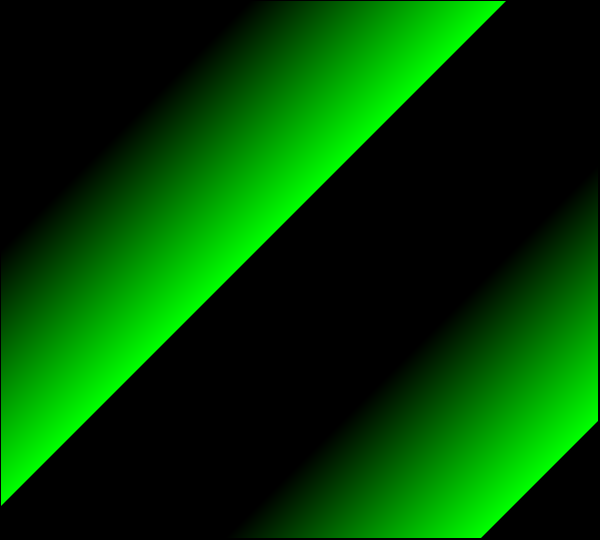

Green Only
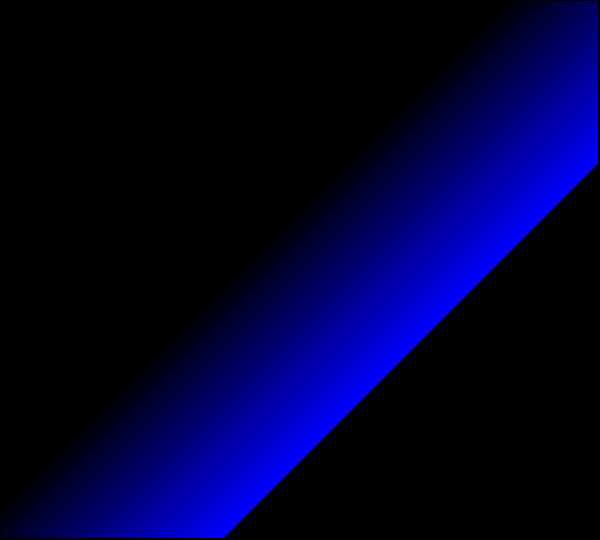

Blue Only
Here are some reference sources that used to create this post
[1] Bayer to RGB
[2] RGB color conversions matrixes
[3] Bayer to RGB algorithm
[4] Bayer Patterns in Digicam CCDs
[5] RGB to gray